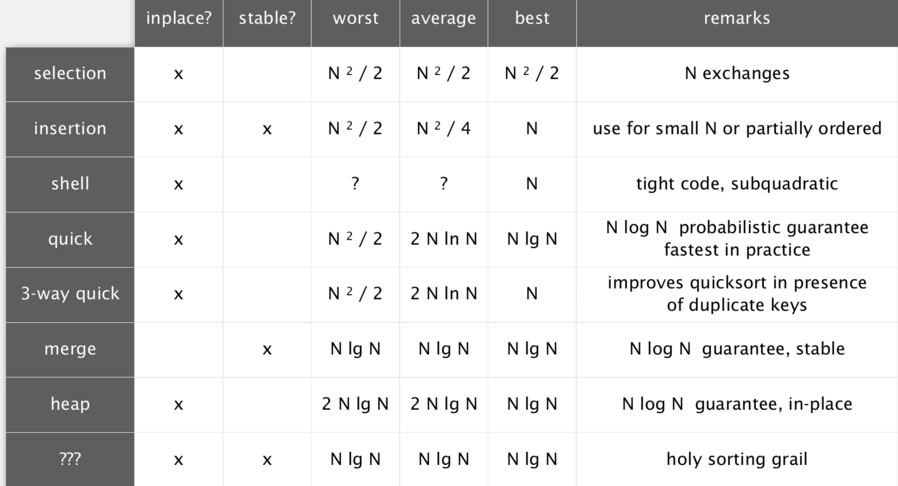
selection sort
insertion sort
merge sort
- 基本思想
- 将数组分成两半
- 递归排序每一半
- 合并两半
具体实现
见附件 Merge.java算法复杂度
- 时间复杂度:Θ(nlogn)
- 空间复杂度:需要额外的空间,等价于数组长度
- 稳定排序
- 改进方法
- 对小数组直接使用插入排序
- 左半边最大值小于右半边最小值,直接结束排序
- 消除复制辅助数组(save time not space)
quick sort
- 基本思想
- 打乱数组 (避免快排出现最坏情况)
- 分块,对于某个元素,元素左边分快中的元素都小于该元素,元素右边分块中的元素都大于该元素
- 递归排序两个分块
- 具体实现
见附件 Quick.java
- Partitioning in-place. Using an extra array makes partitioning easier
(and stable), but is not worth the cost. - Terminating the loop. Testing whether the pointers cross is a bit trickier
than it might seem. - Staying in bounds. The (j == lo) test is redundant (why?),
but the (i == hi) test is not. - Preserving randomness. Shuffling is needed for performance guarantee.
- Equal keys. When duplicates are present, it is (counter-intuitively) better
to stop on keys equal to the partitioning item’s key.
- 特点
- 时间复杂度:θ(nlogn), best case: nlogn, worst case: $0.5n^2$, average case:1.39nlogn
- 空间复杂度:并不需要额外的空间
- 不稳定排序
- 改进方法
- 对小数组直接使用插入排序
- 选择尽量是中点的分割点:int m = medianOf3(a, lo, lo + (hi - lo)/2, hi);
- quick selection
问题描述: 找到一组数据中第k大的数
1 | StdRandom.shuffle(a); |
平均时间复杂度:θ(n)
heap sort
- 基本思想
- 对排序元素构造最大堆积树
- 不断移除最大值
- 具体实现
见附件 heap.java
- build heap using bottum-up method
1 | for (int k = N/2; k>=1; k--) |
- remove the maximum, one at time. leave in array, instead of nulling out.
1 | while (N>1) |
- 特点
- in-palce
- 时间复杂度:θ(NlogN)
- unstable
- make poor use of cache memory